Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by an increase in blood sugar.
The disease occurs as a result of defects in insulin production, a defect in the action of insulin or both factors. In addition to the increase in blood sugar level, the disease is manifested by the release of sugar in urine, abundant urination, thirst increase, fat disorders, protein and mineral metabolism and the development of complications.
Guys
- Type 1 diabetes (autoimmune, idiopathic): Destruction of beta cells of the pancreas, which produce insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus: with the predominant insensitivity of insulin tissues or a predominant defect in insulin production with or without insensitivity.
- Gestational diabetes sugar occurs during pregnancy.
- Other types:
- genetic defects;
- diabetes caused by drugs and other chemicals;
- diabetes caused by infections;
- Pancreatitis, trauma, elimination of the pancreas, acromegaly, izenko - kushinka, thyrotoxicosis and others.
Gravity
- Easy current: There are no complications.
- Average gravity grade: there is damage to the eyes, kidneys, nerves.
- Severe current: Far in diabetes complications.
Diabetes symptoms
The main symptoms of the disease include manifestations such as:
- Abundant urine and greater thirst;
- Increase in appetite;
- General weakness;
- Skin lesions (for example, vitiligo), vagina and urinary tract are especially observed in patients not convicted as a result of emerging immunodeficiency;
- The blurred vision is caused by changes in the media voltage of the eye.
Type 1 diabetes generally begins at an early age.
Type 2 diabetes is generally diagnosed in people over 35 to 40 years.
Diabetes diagnosis
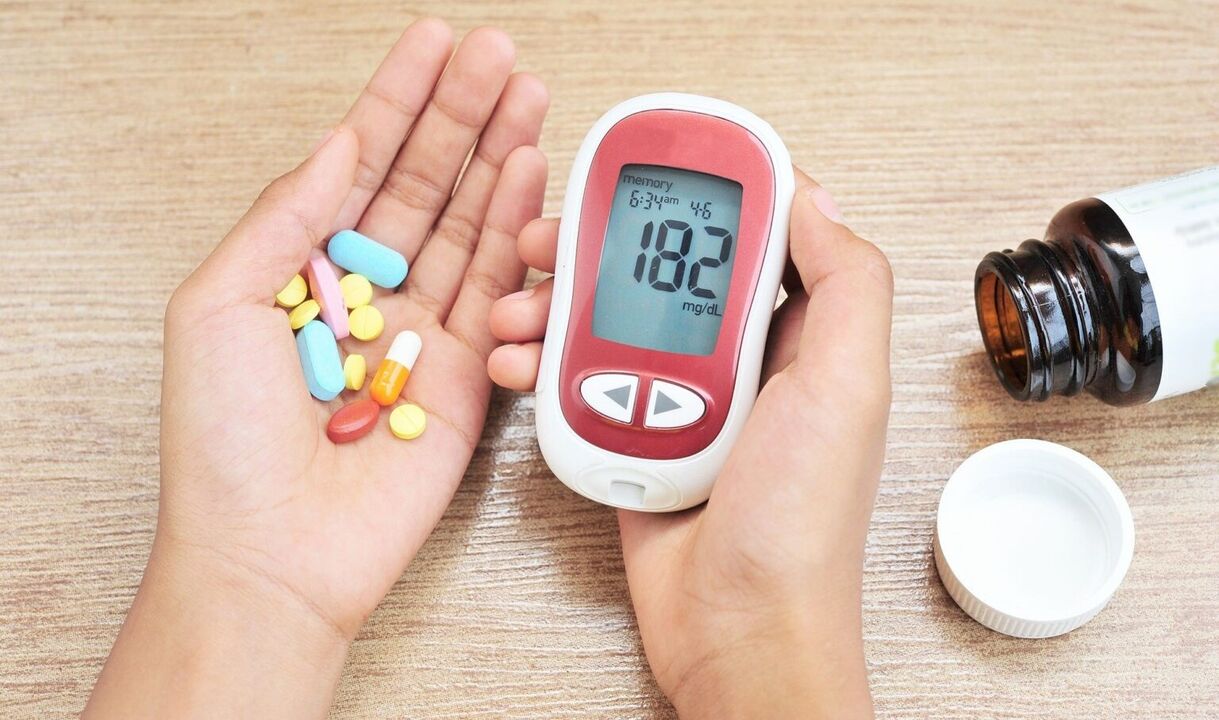
The diagnosis of the disease is based on blood and urine tests.
To make a diagnosis, blood glucose concentration is determined (an important circumstance is a repeated determination of a higher level of sugar and other days).
The analysis results are normal (in the absence of diabetes)
With an empty stomach or 2 hours after the test:
- Venous blood - 3. 3–5. 5 mmol/L;
- Capillary blood - 3. 3–5. 5 mmol/L;
- Blood venous plasma - 4–6. 1 mmol/l.
The analysis results in the presence of diabetes mellitus
With an empty stomach:
- venous blood of more than 6. 1 mmol/l;
- Hair blood more than 6. 1 mmol/L;
- The venous blood plasma is more than 7. 0 mmol/l.
At any time of the day, regardless of the moment of eating:
- venous blood of more than 10 mmol/l;
- capillary blood more than 11. 1 mmol/l;
- The venous blood plasma is more than 11. 1 mmol/l.
The level of blood hemoglobin glyed in diabetes exceeds 6. 7-7. 5 %.
The content of the C peptide allows you to evaluate the functional status of beta cells. In patients with type 1 diabetes, this level is generally reduced, in patients with type 2 diabetes, normally or augmented, in patients with insulinoma, it increases sharply.
Immunorreactive insulin concentration is reduced with type 1, normally or increases with type 2.
The determination of blood glucose concentration to diagnose diabetes is not carried out in the context of acute disease, injury or surgical intervention, in the context of the short -term administration of medications that increase the concentration of glucose in the blood (adrenal hormones, thyroid hormones, shots, beta blockers, etc. ), in patients with zirrosis with zirrosis. liver.
Urine glucose in diabetes appears only after exceeding "renal threshold" (approximately 180 mg % 9. 9 mmol/l). Significant fluctuations on the threshold and a tendency to increase with age are characteristic; Therefore, the definition of glucose in the urine is considered an insensitive and unreliable test. The test serves as a gross reference point for the presence or absence of a significant increase in sugar (glucose) in the blood and in some cases it is used for the daily observation of the dynamics of the disease.
Diabetes treatment
Proper physical activity and nutrition
In a significant part of patients with diabetes mellitus, observe dietary recommendations and achieve a significant decrease in body weight by 5-10 % of the initial blood sugar indicators improve to the norm. One of the main conditions is the regularity of physical effort (for example, walking daily 30 minutes, swimming 1 hour 3 times a week). With the concentration of glucose in the blood>13-15 mmol/L, physical activity is not recommended.
With a light and moderate physical effort that does not last more than 1 hour, additional use of carbohydrates is required before and after the load (15 g of easily digestible carbohydrates per 40 minutes). With a moderate physical effort that lasts more than 1 hour and intensive sports, it is necessary to reduce in 20-50 % of the dose of insulin, acting during and in the next 6-12 hours after physical activity.
The diet in the treatment of diabetes (Table No. 9) aims to normalize the metabolism of carbohydrates and the prevention of fat metabolism.
Treatment with insulin preparations
Insulin preparations for the treatment of diabetes are divided into 4 categories, by the duration of the action:
- Ultra -koro Action (the beginning of the action: after 15 minutes, the duration of the action is 3-4 hours).
- Fast action (the beginning of the action, after 30 min. - 1 hour; duration of the action 6-8 hours).
- The average duration of the action (the beginning of the action is after 1–2. 5 hours, the duration of the action is from 14 to 20 hours).
- Long action (the beginning of the action is after 4 hours; the duration of the action is up to 28 hours).
The insulin appointment modes are strictly individual and are selected for each patient with a dialitologist or endocrinologist.
Methodology to introduce insulin
When insulin is introduced into the injection site, it is necessary to form a skin fold so that the needle enters under the skin, and not into muscle tissue. The skin fold must be wide, the needle must enter the skin at an angle of 45 ° If the thickness of the skin fold is less than the needle length.
When choosing a place for injection, compacted skin areas should be avoided. Injection places cannot be changed non -systematic. They are not injections under the skin of the shoulder.
- Short insulin preparations should be administered in the subcutaneous fat fiber of the abdomen front wall 20-30 minutes before eating.
- Long insulin preparations are introduced into the subcutaneous fat fiber of thighs or buttocks.
- Ultra -short insulin injections are carried out immediately before eating, and if necessary, during or immediately after eating.
Heat and physical activity increase insulin absorption rate, and cold reduces it.